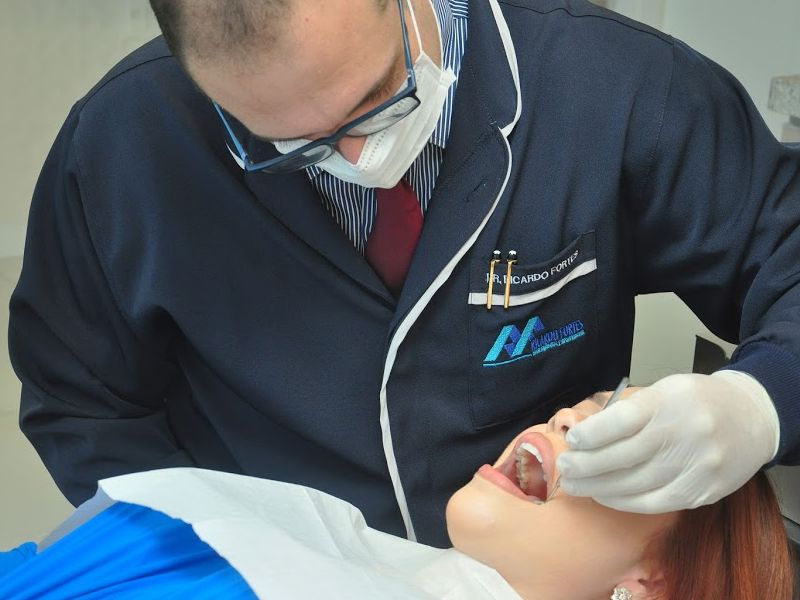
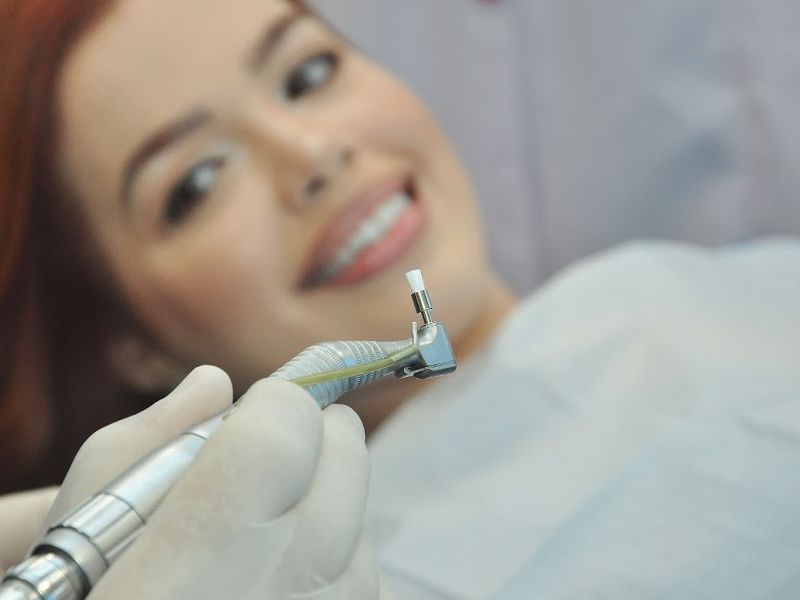
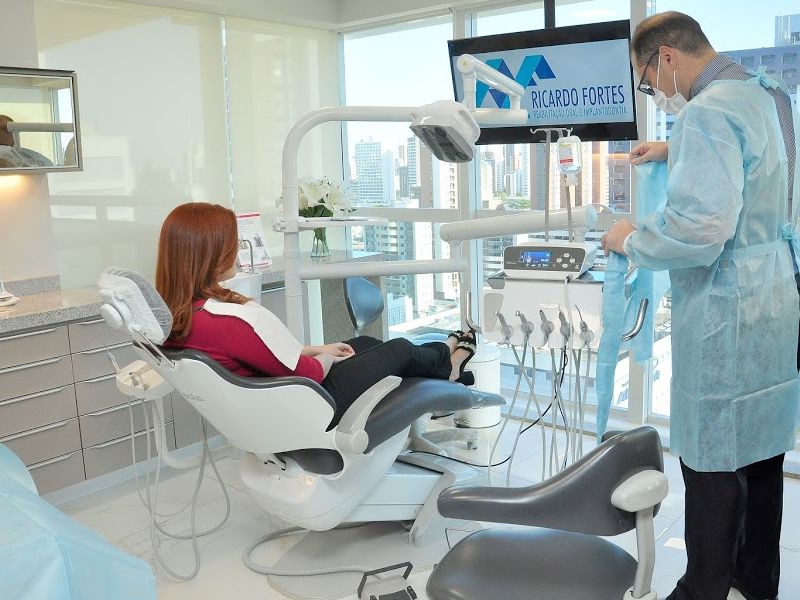
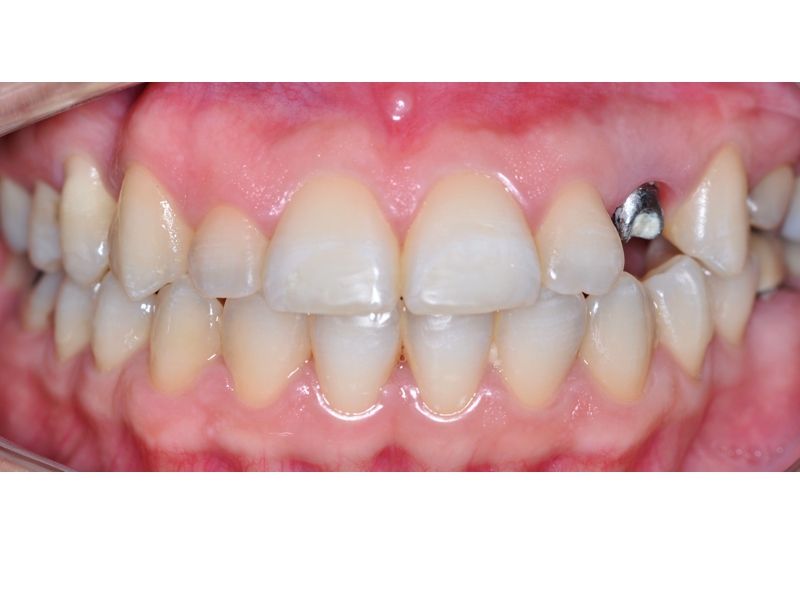
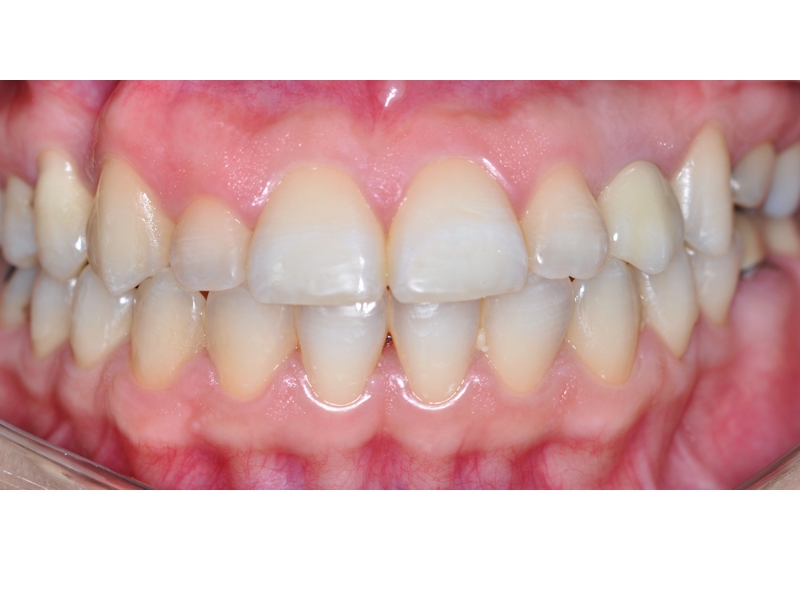
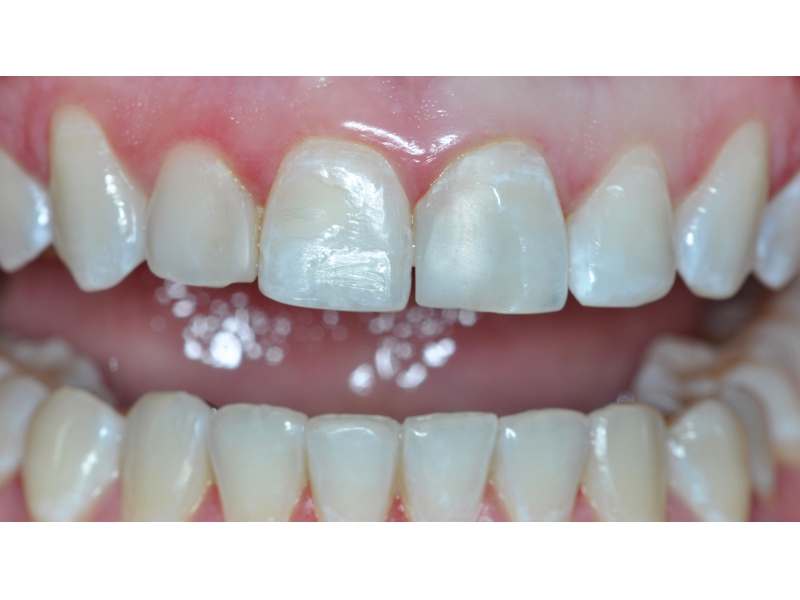
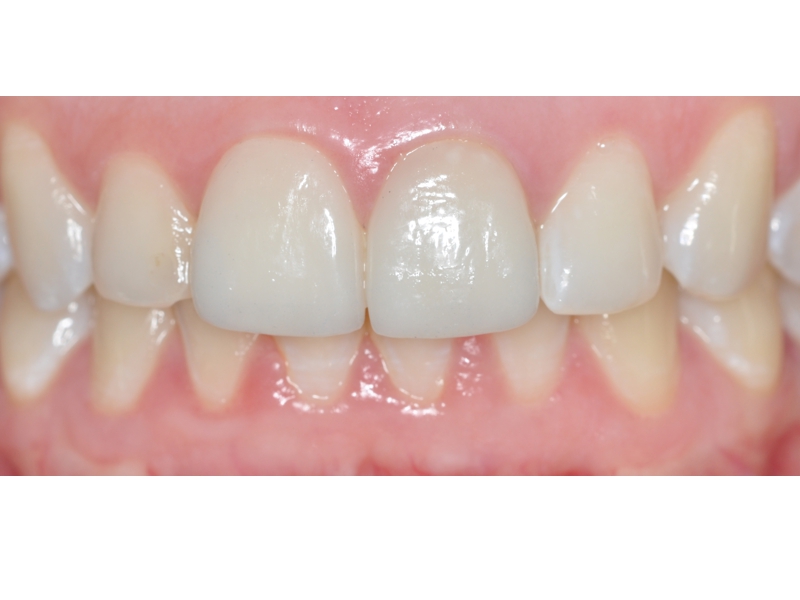
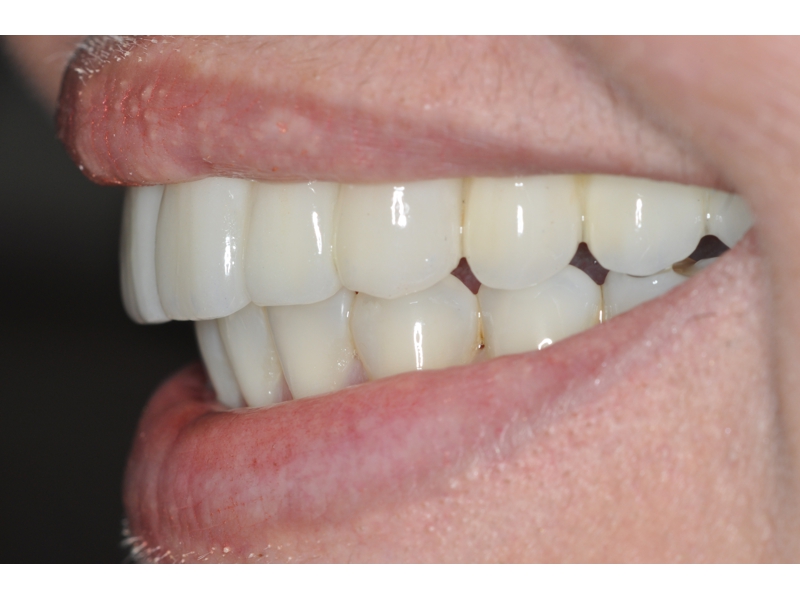
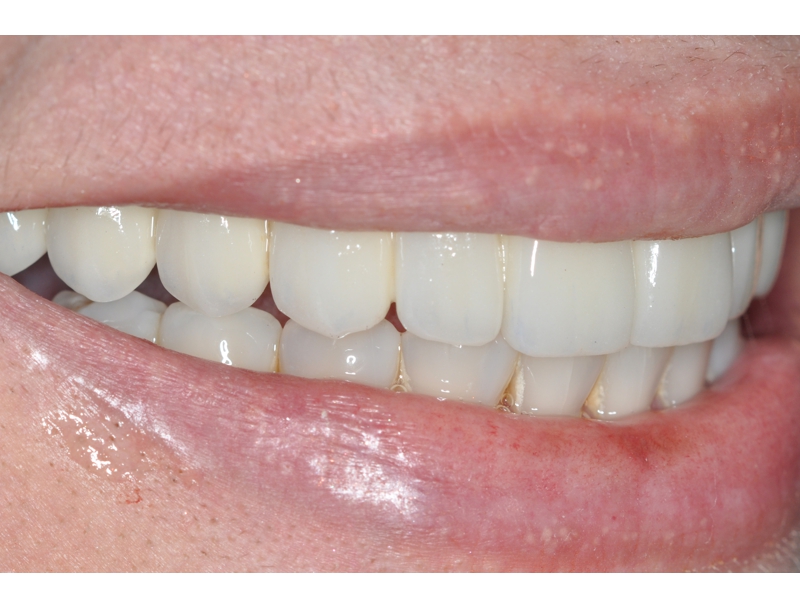
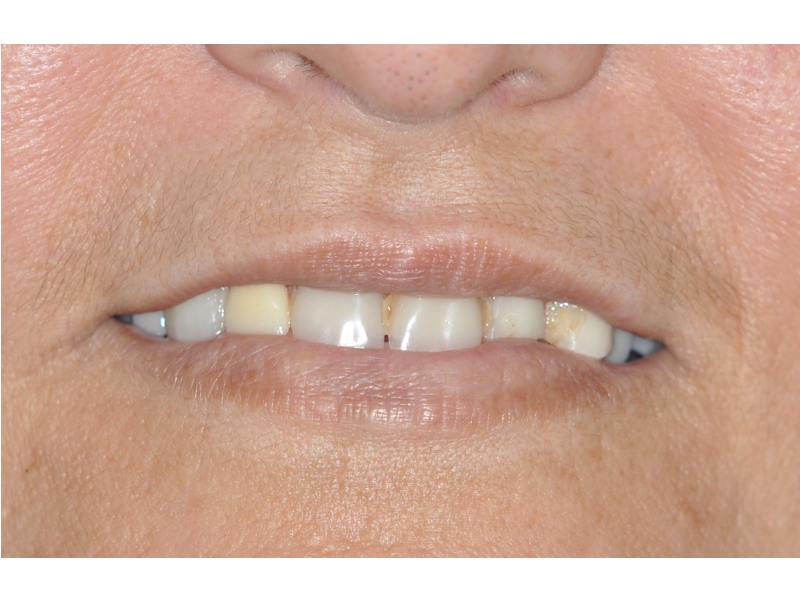
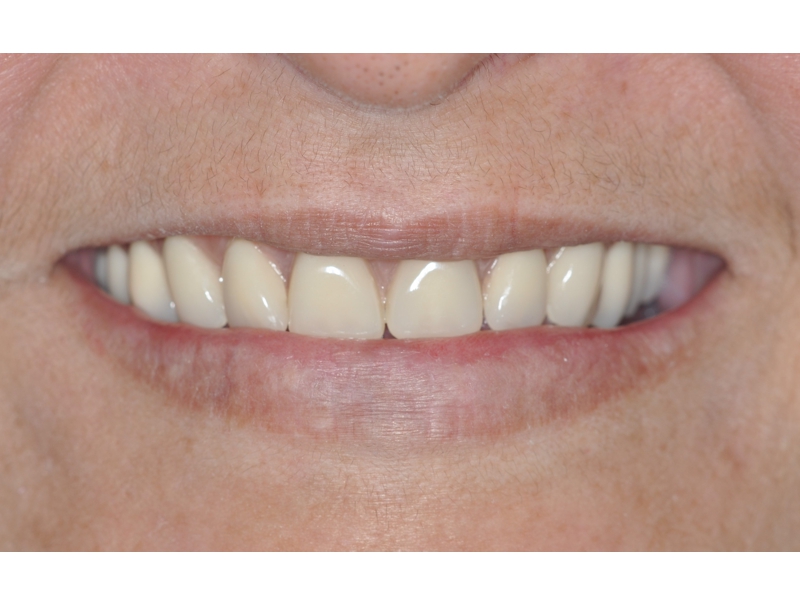
BE WELCOME!
It is a great pleasure to have you on our website. Our main objective is to improve your quality of life and personal well-being.
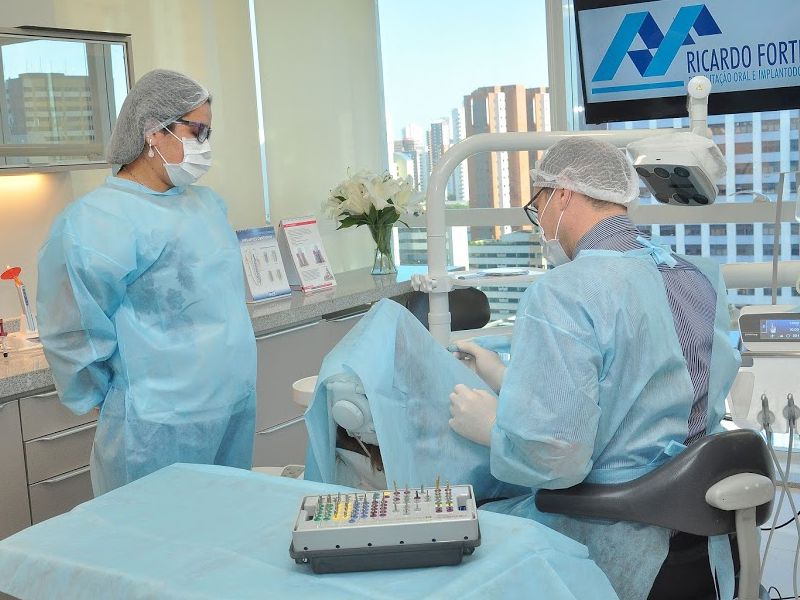
We have a trained team to offer you comfort, safety and the most modern techniques of oral rehabilitation.
We are located in the city of Fortaleza, Ceará, at Portugal, Meireles neighborhood, Ed. Palladium Business Center rooms 1201 and 1202.
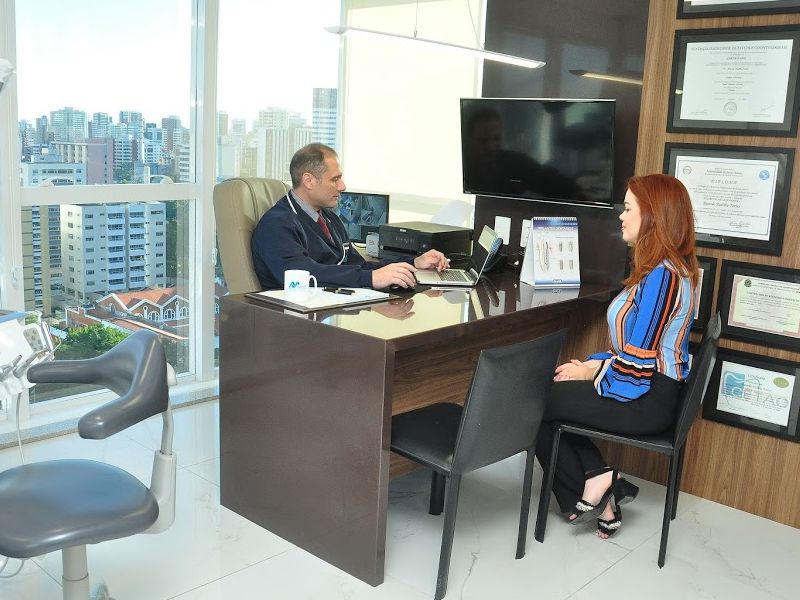
During your visit to our clinic you will be thoroughly evaluated by Dr. Ricardo Fortes and his team, who will advise you on your needs. He will also answer any questions or concerns about the treatment to be performed.

IMPLANTOLOGY
It is the specialty that aims to implant in the jaw and maxilla of a new generation of implants, which are screws ...
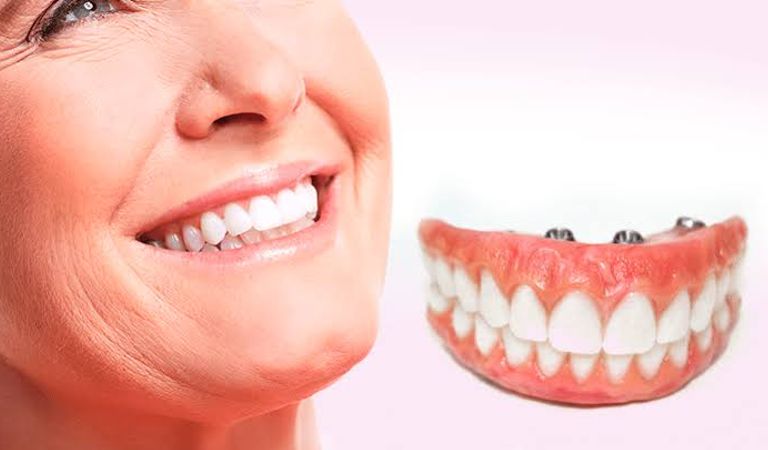
DENTAL PROSTHETICS
Dental prostheses are prosthetic devices that replace lost natural teeth. So that the masticatory system ...

PERIODONTICS
Periodontics is the dental specialization that treats periodontal diseases, that is, soft tissues (gums), bone and ligaments...
The Clinic
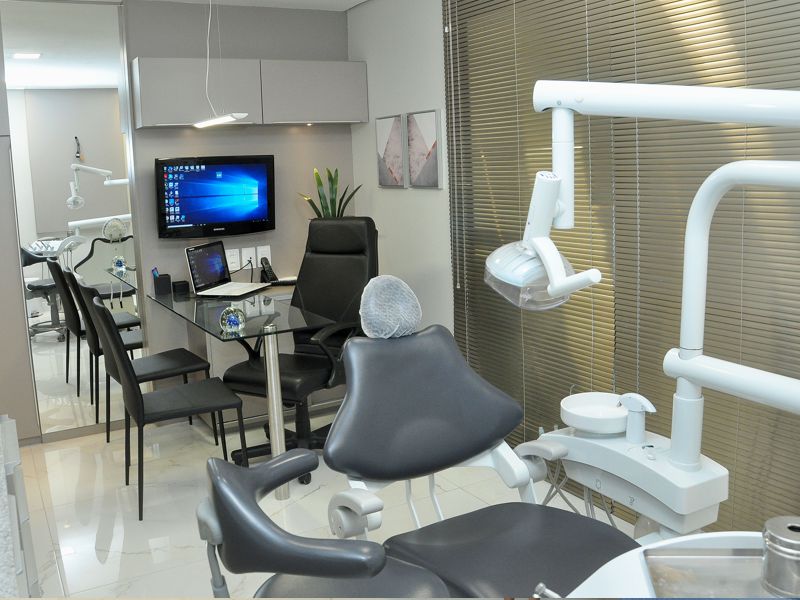
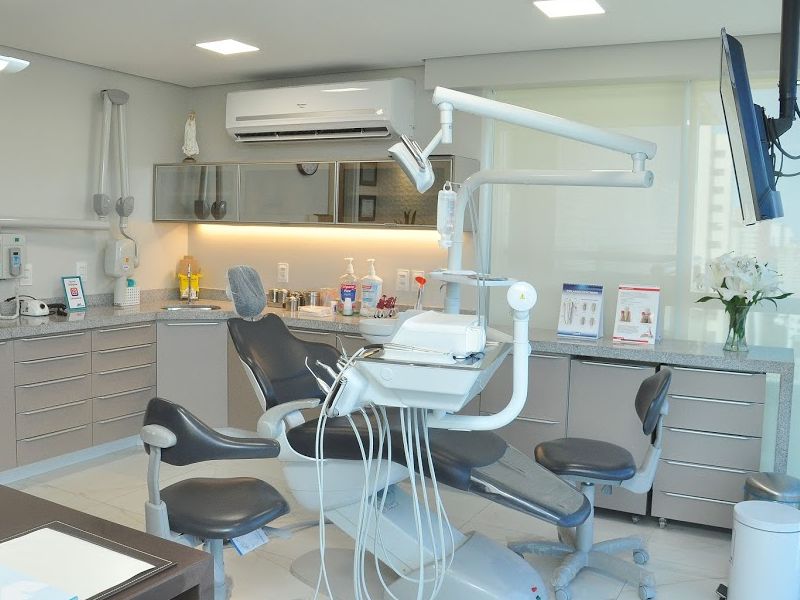
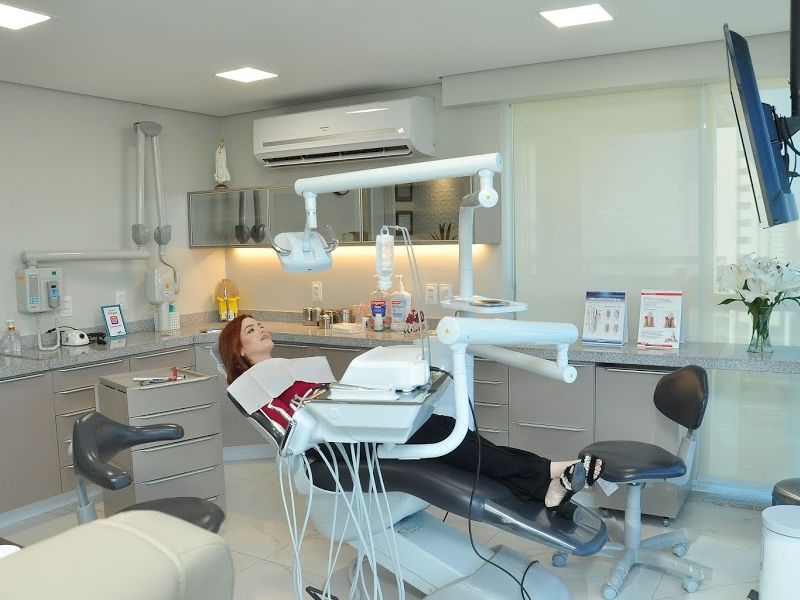
We are an advanced oral rehabilitation clinic, specialized in the areas of Implantology, Dental Prosthesis, Dentistry, Periodontics, Maxillofacial Facial, Orthodontics and Facial Harmonization, directed by Prof. Ms. Ricardo Fortes. Our main concern is the high quality standard, in addition to promptness and professional dynamics with our patients.
The clinic has a modern infrastructure and the latest equipment, helping more and more people to benefit from the improvements that the most modern treatments in the field of oral rehabilitation can provide them.
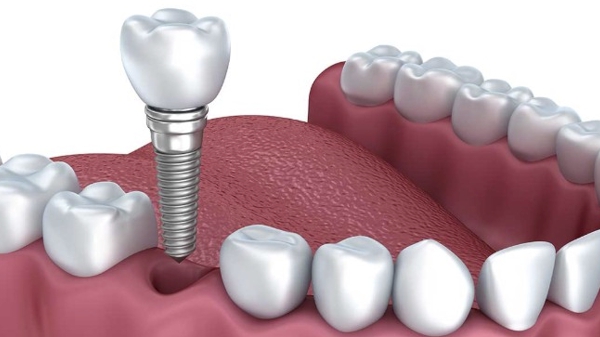
IMPLANTOLOGY
It is the specialty that aims to implant a new generation of implants in the mandible and maxilla, which are titanium screws, placed in edentulous areas that function as artificial roots and have the capacity to exercise masticatory functions in a similar way to natural teeth.
Titanium is the metal used in the manufacture of oral implants, in addition to being highly resistant, it is also "biocompatible", that is, it can remain in the human body without rejection or damage to bone tissue.
Within the dental specialties, it is the area that has shown the greatest evolution in recent years, becoming an important resource in oral rehabilitation. Research indicates that more than 500,000 dental implants are performed worldwide each year, and that success rates are approximately 95 to 98%.
DENTAL PROSTHETICS
Dental prostheses are prosthetic devices that replace lost natural teeth. For the masticatory system to function properly, teeth need to be in balance in the upper and lower dental arches.

The loss of a single tooth unbalances this system of forces, and the teeth move to migrate to compensate for the loss. Spaces are created, unevenness occurs and chewing and aesthetics suffer, teeth need to be replaced. There are basically four types of prostheses:
Fixed prothesis- It is the partial or total restoration of the crown of a tooth, when it is called unitary fixed prosthesis, or the replacement of one or more missing teeth, when it is called fixed partial prosthesis (or "fixed bridge"). These are fixed on the patient's teeth, previously prepared to receive it, rehabilitate him to chew, speak or smile.
Removable partial denture - It is a prosthetic device that replaces the natural teeth lost in the jaws, in which some natural teeth still remain, therefore, with partial loss of teeth. It is called removable because it can be removed by the wearer at any time.
Mobile total prosthesis - Popularly known as dentures, they are substitutes for missing teeth that can be removed and replaced in the mouth. Although it takes some time for the person to get used to using them, and although they are never exactly like natural teeth, today they offer a more natural appearance and greater comfort when compared to those of a few years ago.
Implant prosthesis- There are two types of implant prostheses: fixed or removable. Prostheses on fixed implants are made so that they are no longer removed (cemented) or removed only by the dentist (screwed).
The prostheses on removable implants should always be removed by the patient for hygiene. The latter are attached to the implants through attachments or fittings, which serve to retain the prostheses during use.
The indication for the type of prosthesis must be made by the professional, and can be changed during treatment, depending on several clinical and organic factors. Planning is individual and variable, it is the most important stage of treatment.
DENTIST
It is the branch of dentistry that operates in the field of cosmetics and dental restoration. Among other services, professionals in this specialty deal with teeth whitening, use of direct and indirect resins, laminated veneers, ceramic inlays / onlays (aesthetic blocks) and aesthetic restorations. /h6>
We can include in this specialty dental contact lenses or ceramic laminates, which are ultrafine ceramic structures, which can be only 0.2 mm thick, thus enabling a highly aesthetic and minimally invasive treatment, with minimal wear or in certain situations no dental wear
Contact lenses are usually indicated for aesthetic reasons, being able to correct from small dental imperfections to anterior teeth with small fractures or with diastemas.
They can also be used to disguise dental stains and small discolorations. It focuses on aesthetics, although the restoration of teeth is also an important measure for individual health, since the permanence of cavities can cause problems at various levels, in addition to creating problems in chewing food
PERIODONTICS
Periodontics is the dental specialization that treats periodontal diseases, that is, soft tissues (gums), bone and ligaments, structures that support teeth.
Keeping plaque under control, otherwise, we can have inflamed tissues and consequent tooth loss.
plaque control must also occur in the pre-installation phase of the implants and in the post-installation phase of the permanent prosthesis, which are key factors for the longevity of dental implants.

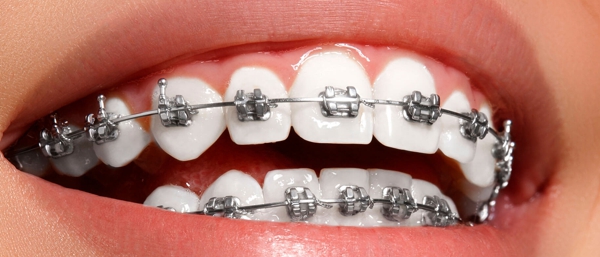
ORTHODONTICS
Orthodontics is the dental specialty that corrects the position of the teeth and jaw bones positioned inappropriately. Crooked teeth or teeth that do not fit properly are difficult to keep clean and can be lost early due to deterioration and periodontal disease.
They also cause additional stress to the chewing muscles which can lead to headaches, TMJ syndrome and pain in the neck, shoulders and back.
Crooked or badly positioned teeth also impair your appearance. Orthodontic treatment makes the mouth healthier, provides a more pleasant appearance and teeth with the possibility of lasting a lifetime.
Oral Maxillofacial Surgery
Buccomaxillofacial Surgery and Traumatology (CTBMF) is the specialty that aims at the diagnosis and surgical and adjuvant treatment of diseases, traumas, injuries and congenital and acquired abnormalities of the masticatory apparatus and attachments, as well as associated cranio-facial structures .
Orthognathic surgery, on the other hand, is a branch of CTBMF that corrects the deformities within the face, in which only orthodontics would not provide the best aesthetic-functional result. Surgical techniques involve osteotomies in the mandible and maxilla in order to reposition the entire middle third of the face, mandible or dental segments to the most appropriate position.
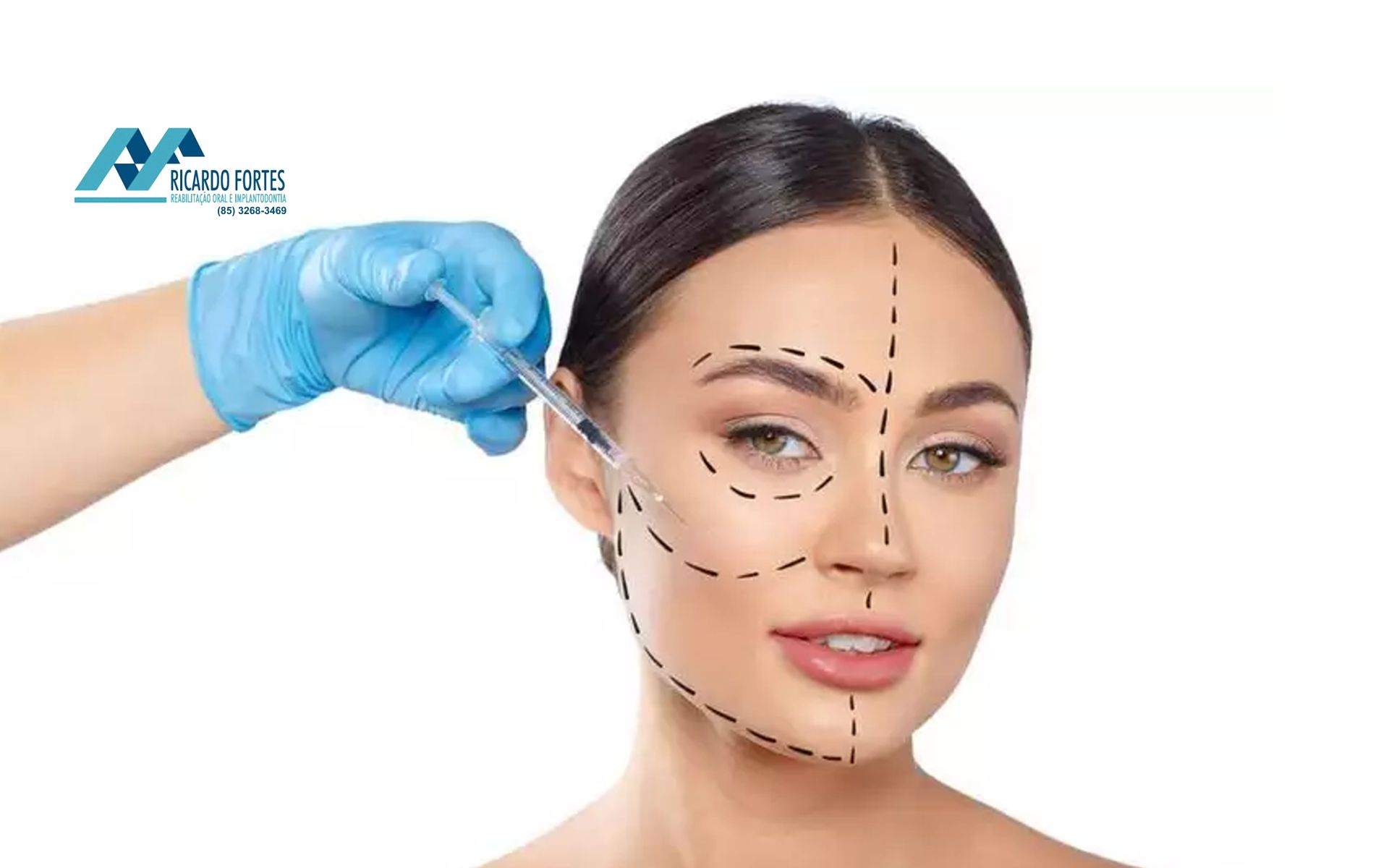
FACIAL HARMONIZATION
Orofacial harmonization or facial harmonization is a set of procedures performed by the dentist responsible for the aesthetic and functional balance of the face.
After consultation, facial harmonization is directed according to the patient's complaints. That is, what bothers you and wants to be improved. Example: for filling and botulinum toxin (botox) we need to apply a topical anesthetic before the product. If it is a bichectomy, it is necessary to do some tests, as it is a surgery.
Abelow, know some facial harmonization techniques:
-Facial filling: consists of applying hyaluronic acid to the subcutaneous layer to hydrate and restore volume to the skin. The filling corrects the furrows and softens the appearance of the Chinese mustache, for example;
- Botox : the function of the butolin toxin is to paralyze the muscle region in order to reduce expression lines and smooth out wrinkles;
- Bichectomy: is the removal of a small amount of fat from the cheeks under local anesthesia. All the above techniques are intended to improve facial aesthetics according to the patient's choices, valuing the face with balanced and more symmetrical features .
How long does it last
Botulinum toxin lasts for about six months. The filling with hyaluronic acid and collagen biostimulators, around a year to a year and a half. As a bichectomy is a surgery, retouching is not necessary.
When indicated
After the age of 25, the person begins to feel the effects of aging. The Chinese mustache, for example, can show signs on the face. Thus, at the age of 40, the effects are visible and people seek more for facial harmonization. In theory, anyone can do it, but they need to check that they are in good health and that they have no systemic contraindications. Botox is also indicated for other solutions, such as bruxism (clenching teeth) causing headaches.
SCHEDULE YOUR CONSULTATION
Smile again! Here, at Dr. Ricardo Fortes' clinic you will find the necessary treatment for your case and with easy payment!
OUR TEAM
Meet the professionals and their specialties:

DR. RICARDO FORTES
CRO CE: 4582
- Master in Implantology - UNISA / SP.
- Specialist in Dental Prosthesis - FOB / USP.
- Invited Professor of the Specialization Course in Implantology - UNIGÁ / SP.
- Postgraduate in Implantology - USP / SP.
- Postgraduate in Implantology - CETAO / SP.
- Postgraduate in Dental Prosthesis - CETAO / SP.
- Postgraduate in Advanced Surgery in Implantology - Biomet 3i / SP.
- Postgraduate in Implantology - Biomet 3i / SP.
- Postgraduate in Prosthesis on Implants - Biomet 3i / SP.
- Member of the American Academy of Osseointegration.

DR. LEANDRO DE ARAUJO BENTO
CRO CE: 6736
- Residency in Maxillofacial Surgery
- UFMS University Hospital.
- Specialist in Oral Maxillofacial Surgery and Traumatology
- Brazilian College of Surgery and Traumatology BMF.
- 1st Lieutenant Dentist of the Brazilian Army - HGeF.
- Adjunct Surgeon at Fortaleza General Hospital
- HGeF. - Postgraduate in Implantology - IEO / BAURU.
- Postgraduate in Therapeutic Pharmacology - ODONS / PR.

PROF. WANDER KOBAYASHI
CRO SP: 53015
- Graduated from the Faculty of Dentistry of Bauru
- USP. - Specialist in Oral Maxillofacial Surgery and Traumatology
- Union of Dentists of the State of São Paulo.
- Specialist in Implantology - APCD / SBC. - Master in Implantology - UNISA / SP.
- Responsible for the Maxillofacial sector at Hospital Albert Sabin / São Paulo.
- Coordinator of the specialization course in Implantology at UNINGÁ / SP.
- Coordinator of the improvement course in Implantodontics at UNINGÁ.
- Advanced Clinical Residence in Orofacial Harmonization - Odonto Partners / SP.
- Qualification in Ozonotherapy - UNINGÁ / Maringá
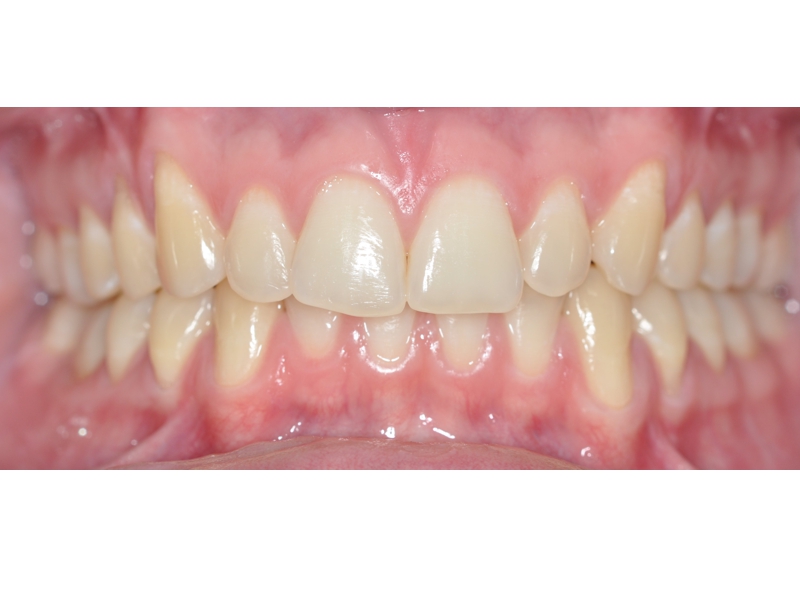
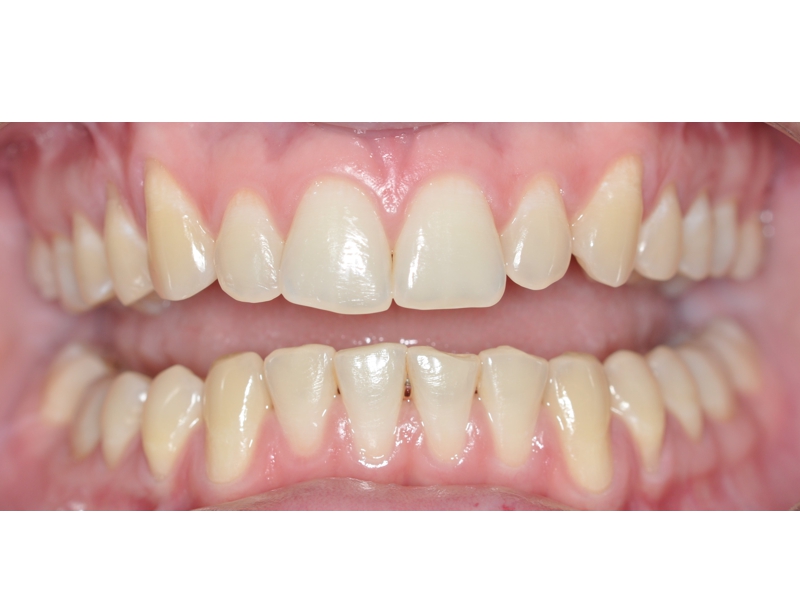
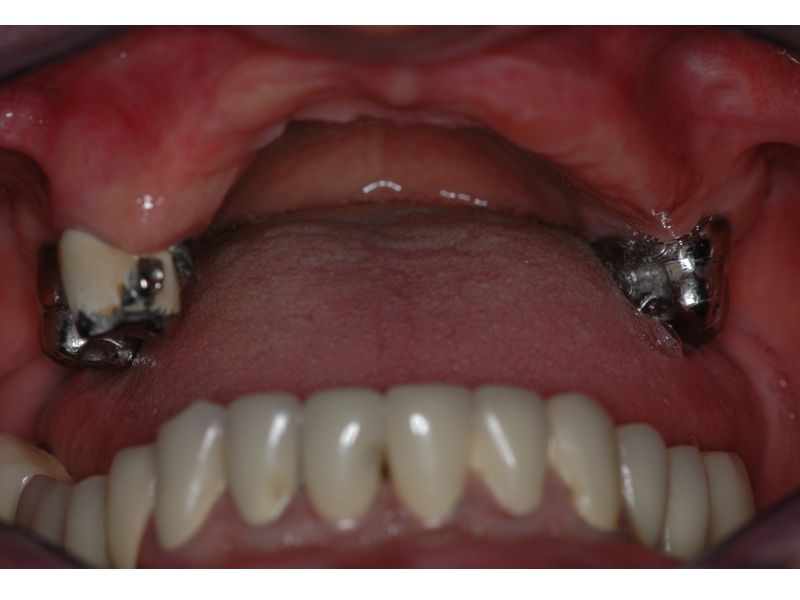
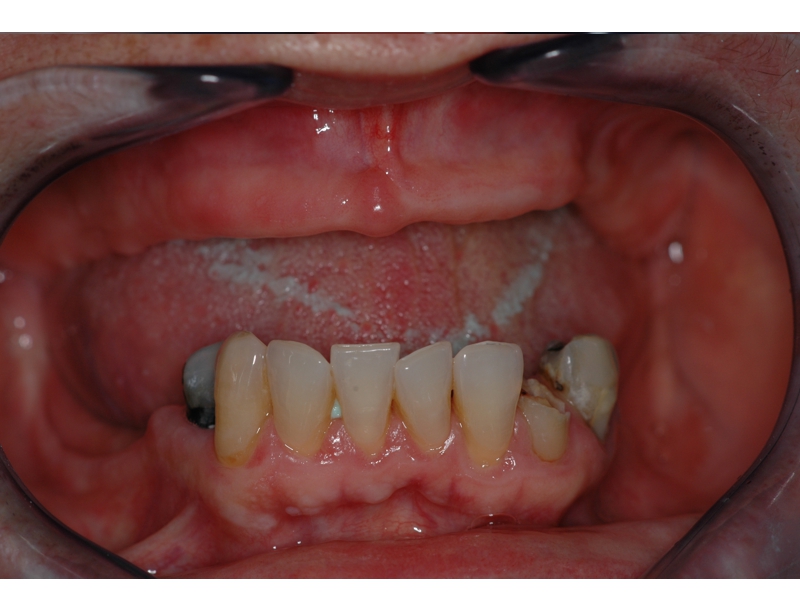
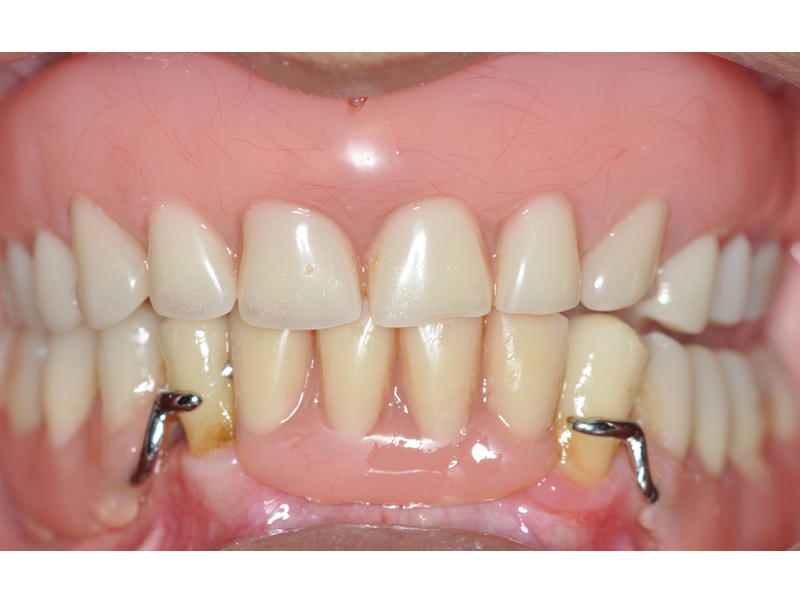
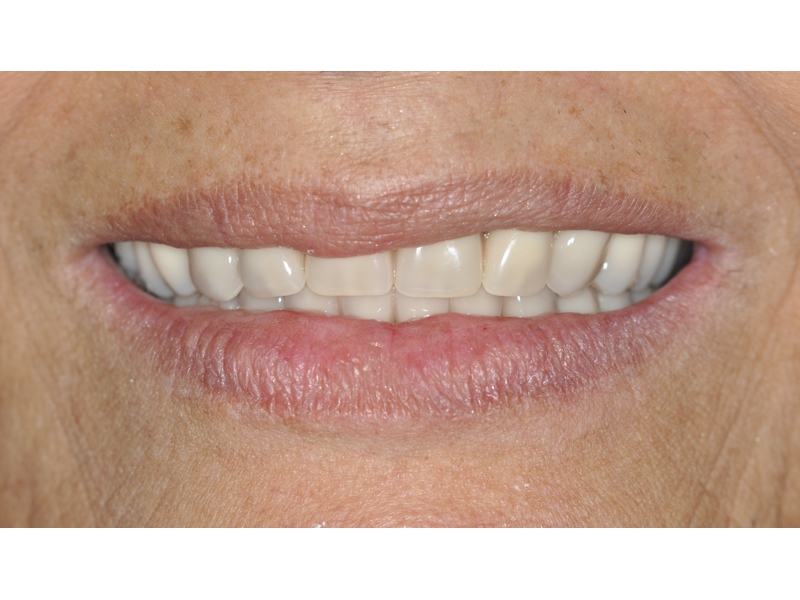
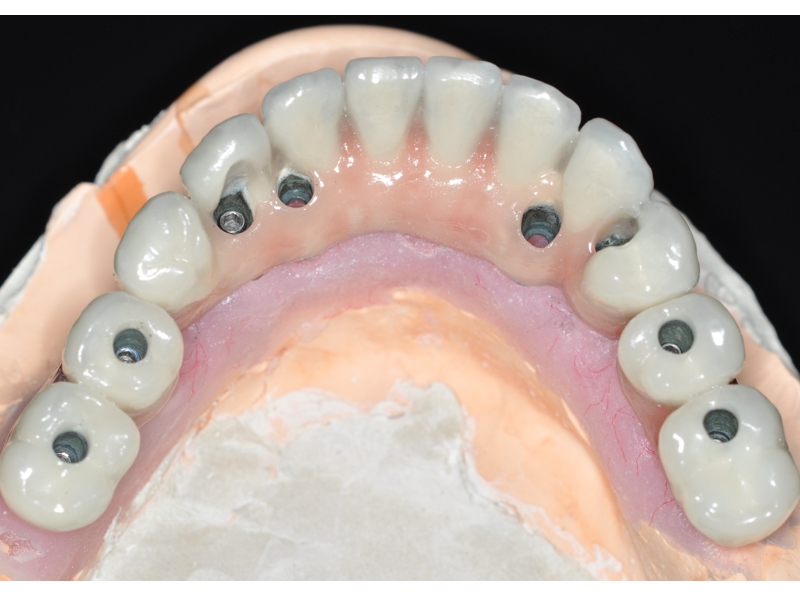
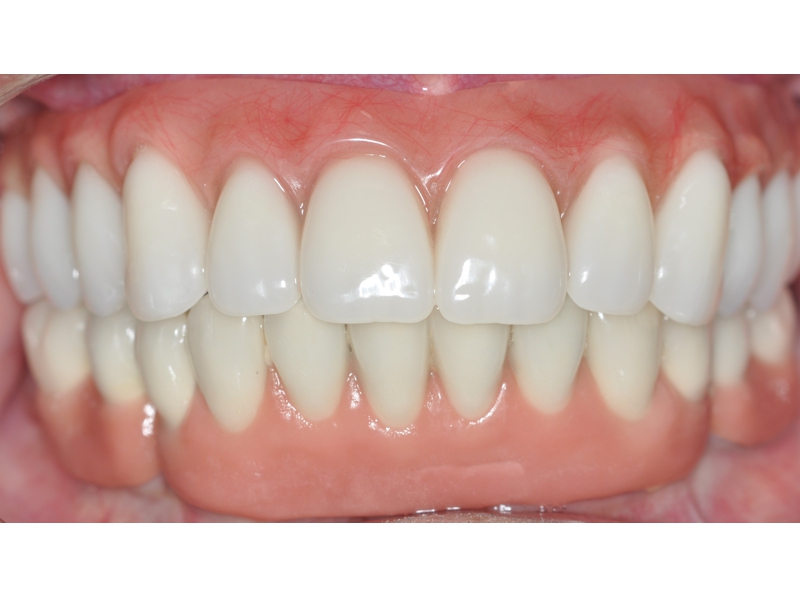
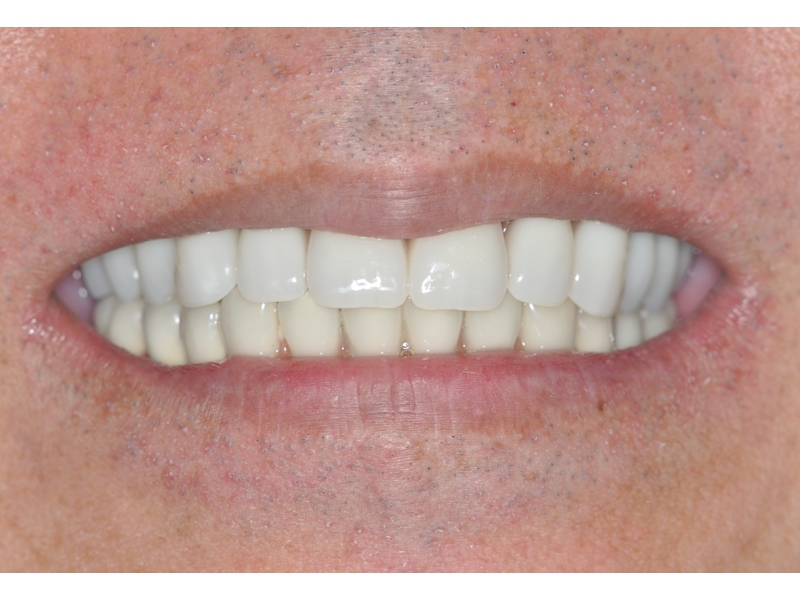
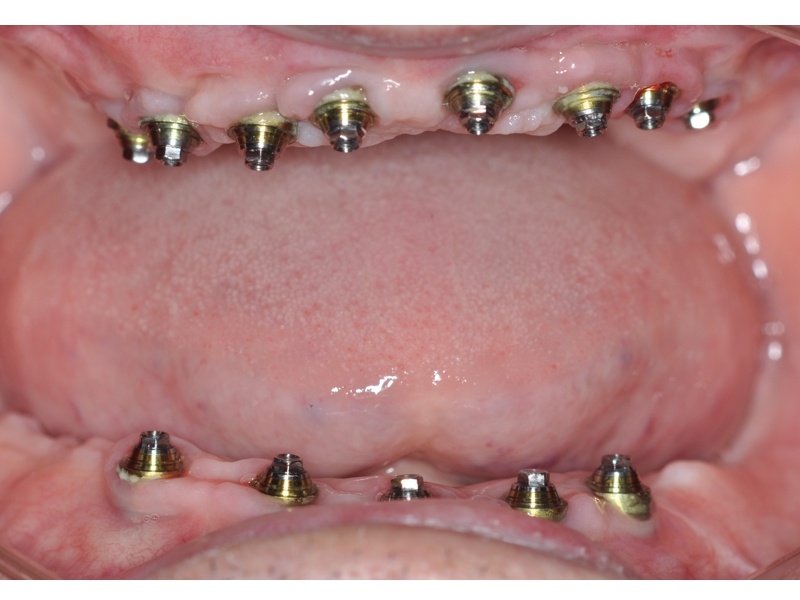
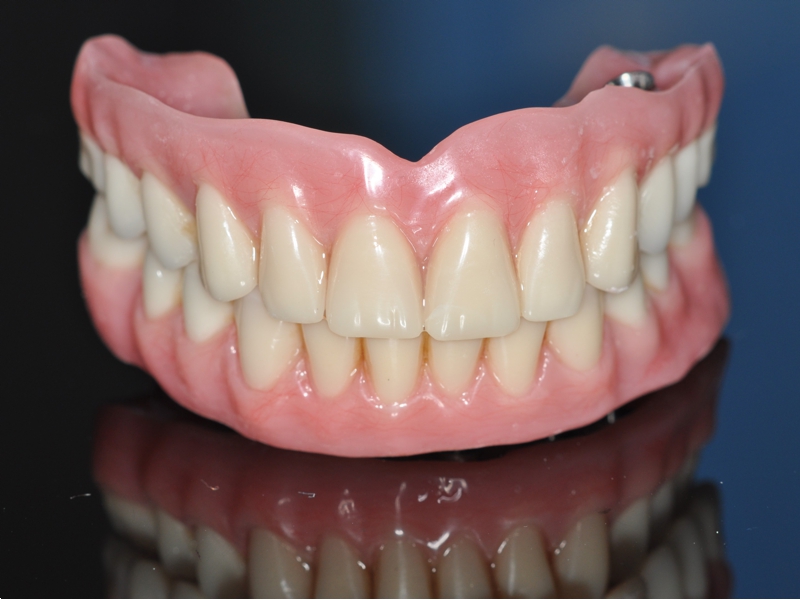
CLINICAL CASES
Higher Protocol + Lower Protocol
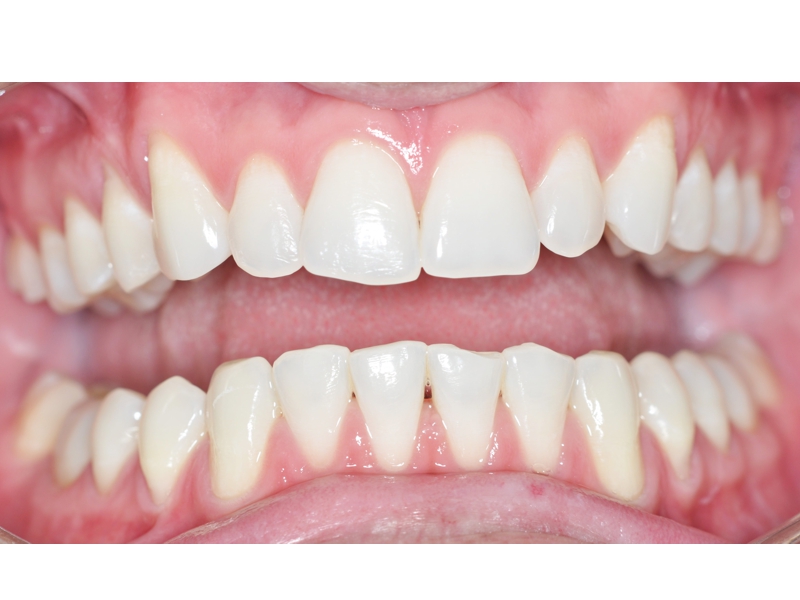
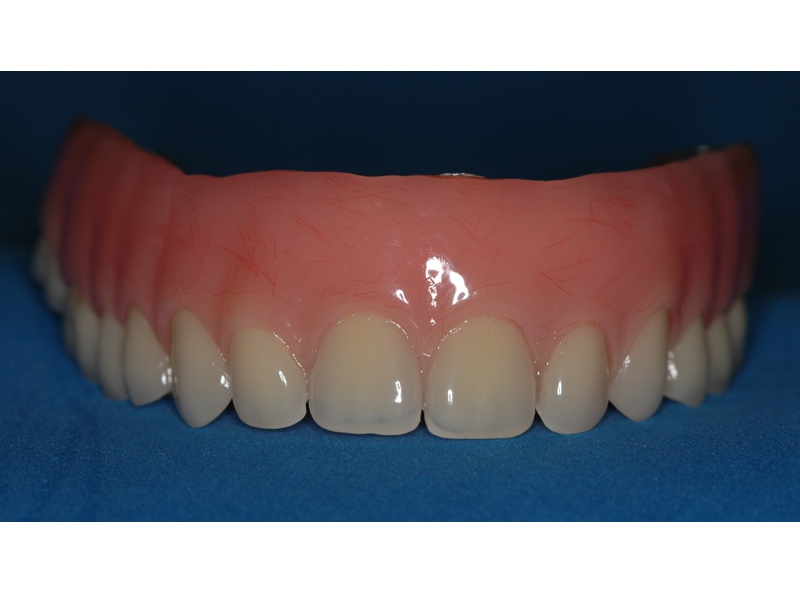
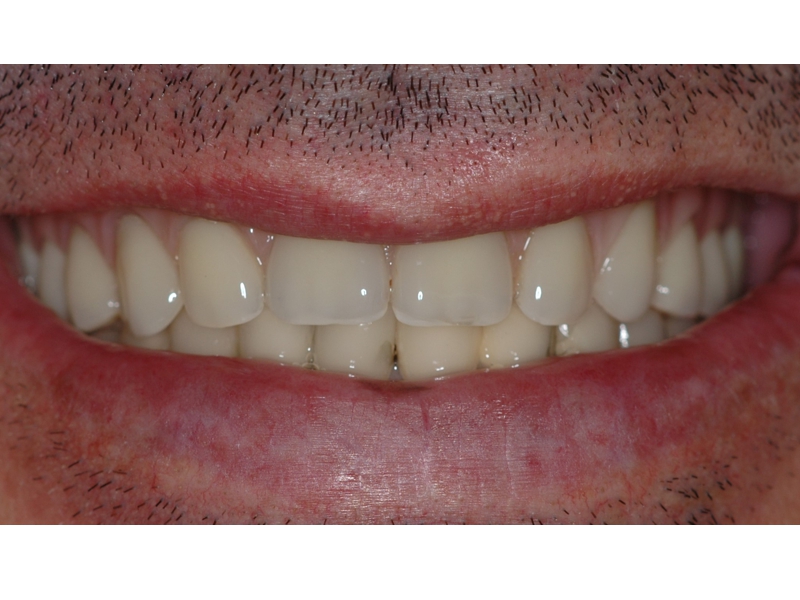
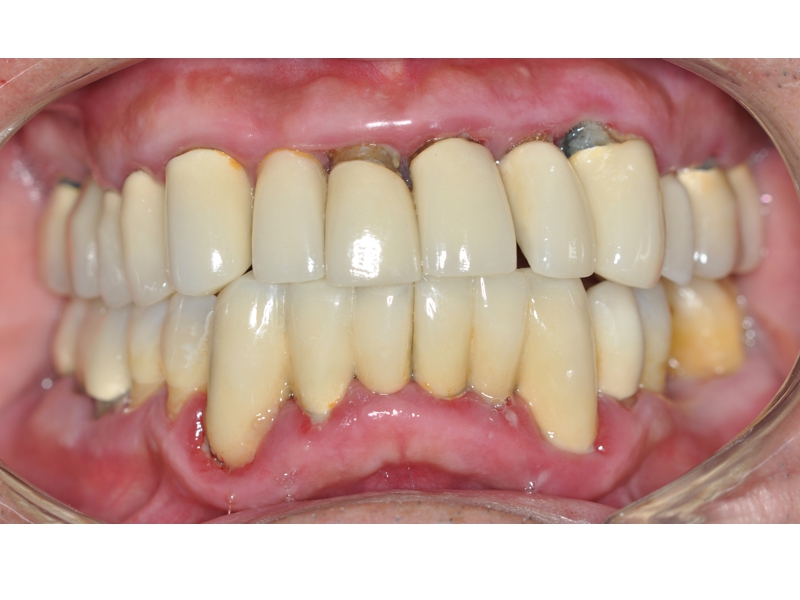
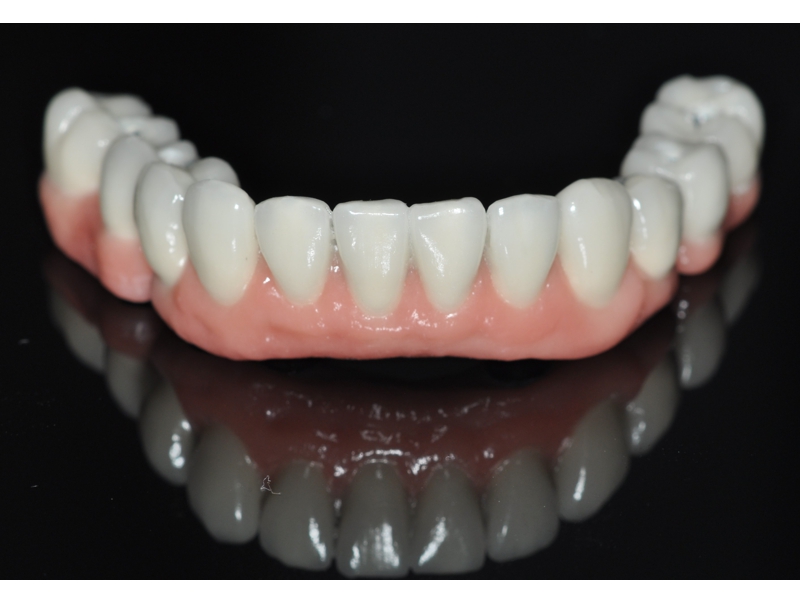
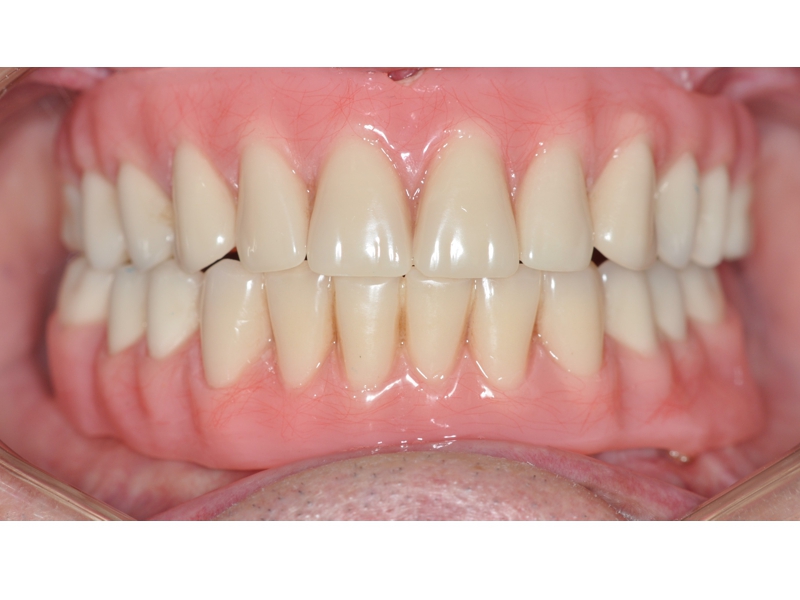
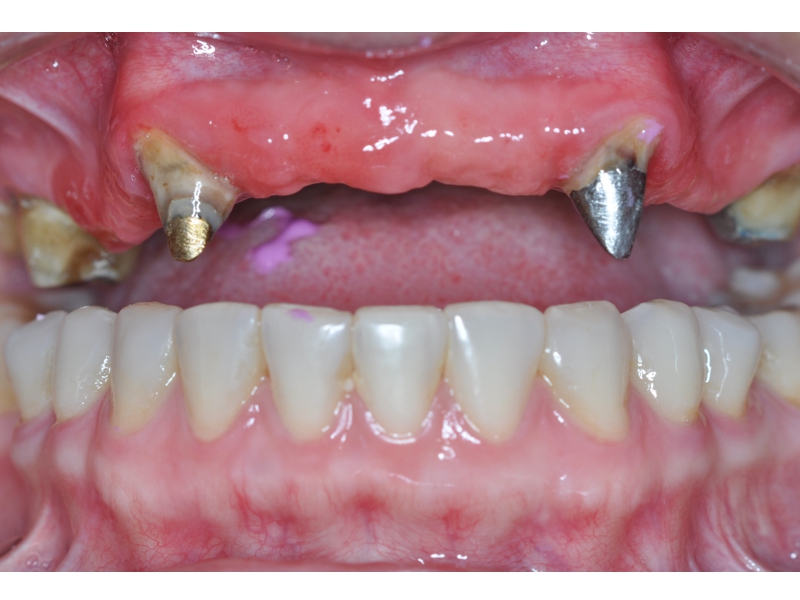
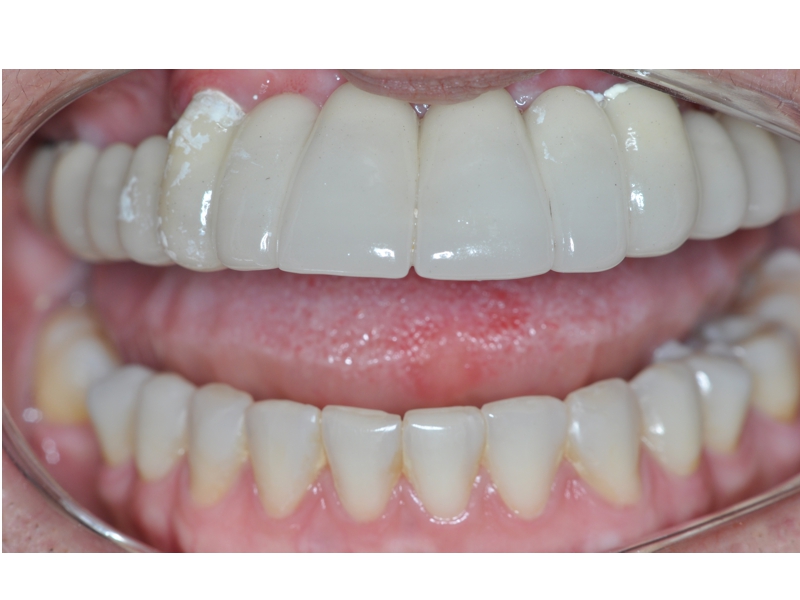
CLINICAL CASES
Oral Rehabilitation Superior Zirconia
PUBLICATIONS
1. KOBAYASHI, W. C.; UCHOA, D. C.; FORTES, R. P.. Histomorphological analysis of bone healing in implants with growth hormone application. Clinical-Scientific Dentistry (Print), v. 11, p. 133-138, 2012
2. FORTES, R. P.; KOBAYASHI, W. C.. Fresh frozen bone from a bone bank: A viable alternative for bone reconstructions. Revista Brasileira de Implantodontia, v. 17, p. 05-06, 2011.
3. FORTES, R. P.; KOBAYASHI, W. C.; BELTRAO, P. R. P.; BORGHI, O.; BEZERRA NETO, Z.. Immediate loading in a type 2 diabetic patient: clinical case report and 2-year follow-up. Brazilian Journal of Implantology, v. 17, p. 05-09, 2011.
4. FORTES, R. P.; FORTES, M. R.; BEZERRA NETO, Z.. Diabetes Mellitus patients: diagnostic and control guidelines. Revista ABO Nacional, v. 17, p. 44-47, 2009.
5. FORTES, R. P.; MACHADO, M. S. S.; EDUARDO, J. V. P.. Work sequence under immediate load, both in the maxilla and in the mandible. Review of EAP / APCD, v. 62, p. 50-56, 2008.
6. FORTES, R. P.; KOBAYASHI, W. C.; SENDYK, W. R.; ROMAO JUNIOR, W.. Comparative analysis of loosening of abutments connected to Morse taper implants, after mechanical cycling. Implant News, Vol. 5, p. 639-645, 2008.
7. FORTES, R. P.; KOBAYASHI, W. C.. Morse taper: an alternative for implant rehabilitation. Journal odontonordeste.com, p. 4 - 8, 01 apr. 2007.
Contact
Send your Message


 (85) 99626-8228
(85) 99626-8228